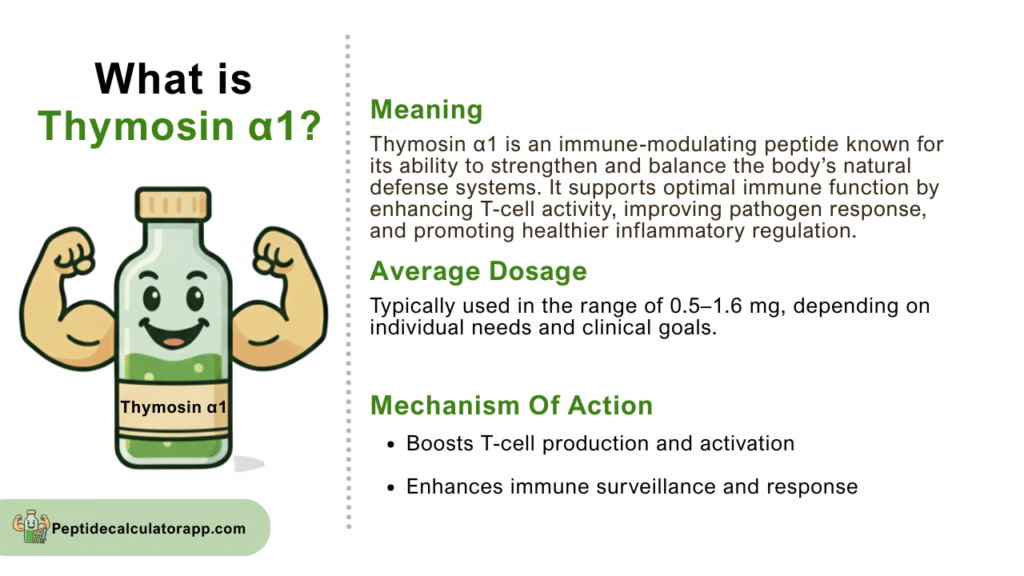
Thymosin α1 is a biologically active peptide hormone that was first isolated from the thymus gland in the 1960s. As a key component of the thymosin fraction 5, this peptide serves as a vital regulator of immune system function. The thymus gland, located behind the breastbone, is responsible for T-cell maturation and immune system development, making thymosin α1 an essential mediator in these processes.
This peptide consists of 28 amino acids and has a molecular weight of approximately 3,108 daltons. Unlike some other peptides that require complex modifications, thymosin α1 maintains its biological activity in its natural form, making it an attractive candidate for therapeutic applications. The peptide has been extensively studied and is approved for medical use in several countries for treating various immune-related conditions.
How Thymosin α1 Works?
Thymosin α1 exerts its effects through multiple pathways within the immune system. The peptide primarily works by stimulating T-cell production and enhancing their function, which is fundamental to maintaining robust immune responses. It binds to specific receptors on immune cells, triggering cascades that lead to improved cellular immunity.
The peptide enhances the activity of dendritic cells, which are crucial for antigen presentation and initiating immune responses. It also promotes the production of various cytokines, including interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma, which are essential for coordinating immune system activities. Additionally, thymosin α1 helps regulate the balance between different types of T-helper cells, ensuring appropriate immune responses without excessive inflammation.
Another important mechanism involves the peptide’s ability to enhance natural killer (NK) cell activity. These cells play a vital role in defending against viral infections and cancer cells. By improving NK cell function, thymosin α1 strengthens the body’s natural surveillance system against potentially harmful cells and pathogens.
Benefits of Thymosin α1
Enhanced Immune System Function
Thymosin α1 is best known for its powerful immune-modulating properties. Clinical research consistently demonstrates its ability to strengthen immune responses, making it especially beneficial for individuals with weakened or compromised immunity. This includes patients undergoing chemotherapy, those recovering from chronic infections, and older adults experiencing age-related declines in immune function. By improving the activity of T-cells, natural killer cells, and other immune components, thymosin α1 helps the body respond more effectively to pathogens.
Support for Chronic Viral Infections
One of the most extensively studied applications of thymosin α1 is in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and C. When used alongside antiviral therapies, it has been shown to improve viral clearance rates, enhance liver health, and reduce inflammation. Its ability to stimulate antiviral immunity makes it a valuable adjunct therapy in managing long-term viral conditions.
Cancer-Related Benefits
Thymosin α1 has also been explored for its role in oncology. By boosting immune surveillance, the peptide enhances the body’s ability to detect and destroy malignant cells. Studies suggest that it can improve treatment outcomes when combined with chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or radiation, while also helping reduce treatment-related immune suppression.
Potential Benefits in Autoimmune Conditions
Thymosin α1 has shown potential in modulating excessive immune activity associated with autoimmune disorders. Rather than suppressing immunity, it helps restore proper regulation—supporting protective immune function while reducing harmful overactivation.
Dosage and Administration
Thymosin α1 is typically administered through subcutaneous injection, as oral administration would result in degradation by digestive enzymes. The standard dosage ranges from 1.6 to 3.2 mg, administered twice weekly, though specific protocols may vary depending on the condition being treated and individual patient factors.
For immune system support, a common protocol involves 1.6 mg administered subcutaneously twice per week for several months. Treatment duration can range from 3 to 6 months, with some protocols extending longer based on clinical response and physician recommendations. The injection is usually given in the abdominal area, rotating injection sites to prevent local irritation.
Patients should receive proper training on injection techniques and sterile procedures. The peptide is typically supplied as a lyophilized powder that requires reconstitution with bacteriostatic water before administration. It’s essential to follow healthcare provider instructions regarding dosage timing and injection procedures to ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Storage and Stability
Proper storage of thymosin α1 is crucial for maintaining its biological activity and therapeutic effectiveness. The lyophilized powder should be stored in a refrigerator at temperatures between 2-8°C (36-46°F) and protected from light. Under these conditions, the powder can remain stable for up to two years from the manufacture date.
Once reconstituted with bacteriostatic water, the solution should be used within 30 days when stored in the refrigerator. It’s important to avoid freezing the reconstituted solution, as this can damage the peptide structure and reduce its effectiveness. The solution should appear clear and colorless; any cloudiness or discoloration indicates degradation and the solution should be discarded.
For travel purposes, the reconstituted peptide can be stored at room temperature for up to 72 hours, though refrigeration is preferred whenever possible. Always use sterile handling techniques when preparing and administering the peptide to prevent contamination and ensure patient safety.
Potential Side Effects
General Tolerability
Thymosin α1 is generally well-tolerated when used under medical supervision. Most individuals experience minimal discomfort, and any side effects that arise are usually mild and short-lived.
Common Side Effects
The most frequent reactions are related to the injection site. These may present as mild pain, slight redness, or temporary swelling. Such effects typically resolve within a few hours without requiring treatment.
Systemic Reactions
Some patients may experience mild systemic symptoms, especially during the early stages of therapy. These can include temporary fatigue, mild flu-like sensations, occasional headaches, or nausea. These reactions often reflect the activation of the immune system and usually diminish as the body adapts to treatment.
Serious Adverse Effects
Serious reactions are rare but can occur. In uncommon cases, individuals may develop allergic responses such as skin rashes, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Although thymosin α1 influences immune regulation, significant autoimmune reactions have not been commonly observed in clinical settings, but careful monitoring is still advisable for individuals with autoimmune conditions.
FAQs
Q1. How long does it take to see results from thymosin α1 treatment?
Ans: Most patients begin to notice improvements in immune function and overall well-being within 4-6 weeks of starting treatment. However, optimal benefits may take 2-3 months of consistent therapy to fully manifest.
Q2. Can thymosin α1 be used with other medications?
Ans: Thymosin α1 generally has good compatibility with other medications, but it’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you’re taking to avoid potential interactions.
Q3. Is thymosin α1 suitable for long-term use?
Ans: Studies have shown that thymosin α1 can be safely used for extended periods under medical supervision. Long-term protocols are often used for chronic conditions or ongoing immune support.
Q4. How does thymosin α1 compare to other immune-supporting treatments?
Ans: Thymosin α1 offers unique advantages due to its natural origin and specific mechanism of action. Unlike broad immunosuppressants or stimulants, it helps modulate immune function rather than simply suppressing or overstimulating it.
Final Thoughts
Thymosin α1 represents a significant advancement in immune system therapy, offering a natural and effective approach to enhancing immune function. Its well-established safety profile and proven therapeutic benefits make it an attractive option for various medical conditions and health optimization goals.
As research continues to unveil new applications for this remarkable peptide, thymosin α1 is likely to play an increasingly important role in modern medicine. Whether used for treating specific conditions or supporting overall immune health, this peptide offers hope for individuals seeking to optimize their immune system function and improve their quality of life.




