Cetrorelix is a third-generation GnRH antagonist that was developed specifically for use in assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedures. This decapeptide analog contains D-amino acids and other modifications that make it resistant to enzymatic degradation while maintaining high binding affinity to GnRH receptors. The peptide was first approved by the FDA in 1999 and has since become a cornerstone medication in in vitro fertilization (IVF) protocols worldwide.
The molecular structure of Cetrorelix allows it to competitively bind to GnRH receptors in the anterior pituitary gland, effectively blocking the natural GnRH signaling pathway. This blockade prevents the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are crucial for natural ovulation but can interfere with controlled ovarian stimulation during fertility treatments.
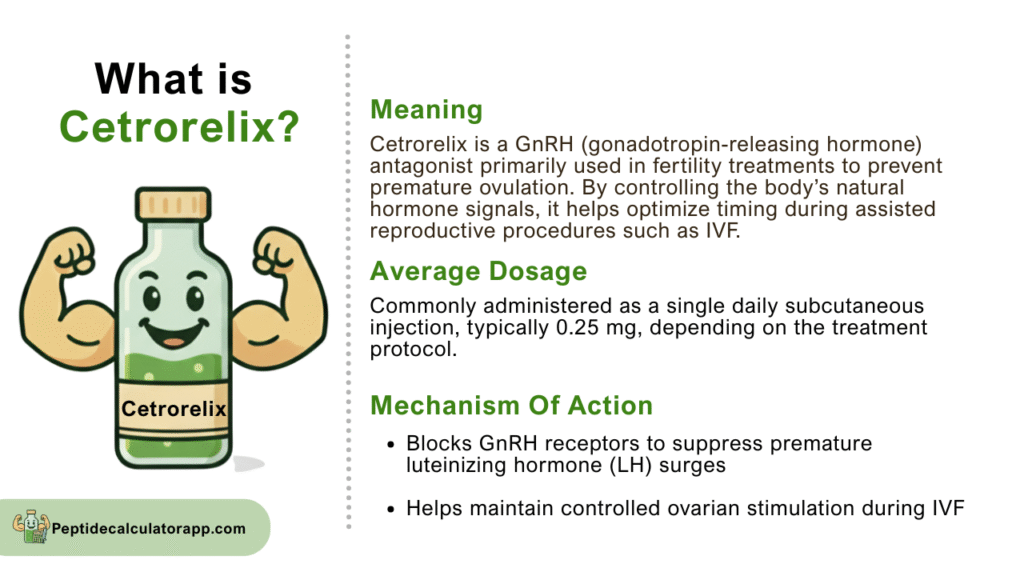
How Cetrorelix Works?
Cetrorelix works through competitive antagonism at the GnRH receptor sites located in the anterior pituitary gland. When administered, the peptide rapidly binds to these receptors with high affinity, effectively blocking endogenous GnRH from triggering its normal cascade of hormonal events. This mechanism is fundamentally different from GnRH agonists, which initially stimulate the receptors before causing downregulation.
The immediate onset of action is one of Cetrorelix’s key advantages. Within hours of administration, LH and FSH levels begin to decrease, providing rapid control over the reproductive hormone axis. This quick response time allows fertility specialists to precisely time the administration relative to other medications in the IVF protocol, ensuring optimal follicular development without premature ovulation.
The duration of action depends on the dose administered, with single-dose formulations providing coverage for 96 hours and multiple-dose regimens offering flexible daily control. The peptide’s pharmacokinetic profile shows rapid absorption after subcutaneous injection, with peak plasma concentrations reached within 1-2 hours and a half-life of approximately 62 hours for the 3mg formulation.
Benefits of Cetrorelix
Prevention of Premature LH Surges
Cetrorelix’s primary clinical advantage is its ability to prevent premature luteinizing hormone (LH) surges during controlled ovarian stimulation. By effectively blocking this early surge, it significantly reduces the likelihood of premature ovulation, thereby improving the chances of successful egg retrieval and embryo transfer. This benefit has been consistently supported by clinical studies and is a key reason why Cetrorelix is widely used in IVF protocols.
Shorter and More Convenient Treatment Protocols
Unlike traditional GnRH agonist protocols—which often require 2–4 weeks of downregulation—Cetrorelix can be introduced partway through the cycle. This reduces the overall treatment duration and minimizes the burden on patients. The shorter protocol is especially advantageous for women with diminished ovarian reserve or those who respond poorly to prolonged hormonal suppression.
Improved Tolerability and Reduced Side Effects
Cetrorelix is generally well-tolerated and is associated with fewer menopausal symptoms than traditional GnRH agonists. Patients experience fewer hot flashes, mood disturbances, and bone density concerns because the peptide does not induce long-term hormonal suppression. This improved tolerability contributes to a smoother and more comfortable IVF experience.
Dosage and Administration
Cetrorelix is available in two primary formulations: a single-dose 3mg depot injection and a multiple-dose 0.25mg daily injection protocol. The choice between these options depends on patient factors, physician preference, and specific IVF protocol requirements. The 3mg formulation is administered as a single subcutaneous injection, typically given when the lead follicle reaches 13-14mm in diameter during ovarian stimulation.
For the multiple-dose protocol, patients receive 0.25mg subcutaneous injections daily, usually starting on stimulation day 5 or 6, or when the lead follicle reaches 12-13mm. This regimen continues until the day of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) administration, which triggers final oocyte maturation. The injection site should be rotated to prevent irritation, and the medication should be administered at approximately the same time each day for consistent hormone suppression.
Proper injection technique is crucial for optimal absorption and efficacy. The medication should be injected subcutaneously into the abdomen, avoiding the area around the navel, or into the upper thigh. The injection site should be clean and dry, and patients should be instructed to inject slowly and steadily to minimize discomfort and ensure complete delivery of the medication.
Storage and Stability
Cetrorelix requires specific storage conditions to maintain its stability and potency. The medication should be stored in a refrigerator at temperatures between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and protected from light. The packaging should remain intact until use, as exposure to light can degrade the peptide and reduce its effectiveness.
Once prepared for injection, the solution should be used immediately and not stored for later use. If traveling, patients should use insulated cooling packs to maintain proper temperature, but the medication should not be allowed to freeze, as this can damage the peptide structure and render it ineffective. Room temperature storage for short periods (up to 3 months) is acceptable, but refrigeration is preferred for optimal stability.
The lyophilized powder formulation generally offers greater stability than pre-mixed solutions, allowing for longer shelf life when stored properly. Patients should always check the expiration date before use and never use medication that appears cloudy, discolored, or contains particles after reconstitution.
Potential Side Effects
Injection Site Reactions
Cetrorelix commonly causes mild to moderate reactions at the injection site. These may include redness, swelling, itching, or bruising. Such effects usually resolve within a few hours to days and can often be minimized through proper injection technique and routine rotation of injection sites.
Systemic Effects
Some patients may experience systemic side effects such as nausea, headache, abdominal discomfort, or fatigue. Mild ovarian enlargement may also occur due to stimulation, which is generally expected during IVF cycles. However, patients should be monitored for signs of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Mood-related symptoms—including irritability or emotional sensitivity—have been reported but are typically less pronounced than with traditional GnRH agonist protocols.
Rare but Serious Reactions
Although uncommon, serious allergic reactions can occur. Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or widespread rash. These reactions require immediate medical attention.
Overall, current research and clinical experience indicate that short-term Cetrorelix use during IVF cycles is safe for most patients and does not pose significant long-term health risks.
FAQs
Q1. Can I inject Cetrorelix myself at home?
Ans: Yes, most patients can self-administer Cetrorelix after receiving proper training from their healthcare team. The subcutaneous injection technique is relatively simple, and detailed instructions are provided with the medication.
Q2. What should I do if I miss a dose of the daily Cetrorelix injection?
Ans: If you miss a dose, contact your fertility clinic immediately. Depending on the timing and your specific protocol, your doctor may adjust your medication schedule or recommend additional monitoring to ensure treatment effectiveness.
Q3. Are there any foods or medications I should avoid while using Cetrorelix?
Ans: There are no specific food restrictions while using Cetrorelix. However, you should inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you’re taking, as some may interact with your fertility treatment protocol.
Q4. How does Cetrorelix compare to other fertility medications?
Ans: Unlike other peptide therapies that focus on different therapeutic areas, Cetrorelix specifically targets reproductive hormone regulation. It offers advantages over traditional GnRH agonists in terms of shorter treatment duration and reduced side effects while maintaining similar efficacy rates.
Final Thoughts
Cetrorelix represents a significant advancement in fertility treatment protocols, offering patients and physicians a reliable, well-tolerated option for preventing premature ovulation during assisted reproductive procedures. Its rapid onset of action, favorable side effect profile, and flexible dosing options have made it a preferred choice in many IVF programs worldwide.
The peptide’s success in clinical practice reflects the importance of precision medicine in reproductive health, where timing and hormonal control are critical factors in achieving successful outcomes. As research continues to refine protocols and identify optimal patient populations, Cetrorelix will likely remain an essential tool in the fertility specialist’s arsenal.
For patients considering IVF treatment, understanding the role of medications like Cetrorelix can help in making informed decisions about treatment options. The combination of clinical efficacy, patient convenience, and safety profile makes Cetrorelix an excellent choice for many individuals pursuing their reproductive goals through assisted reproductive technology.




