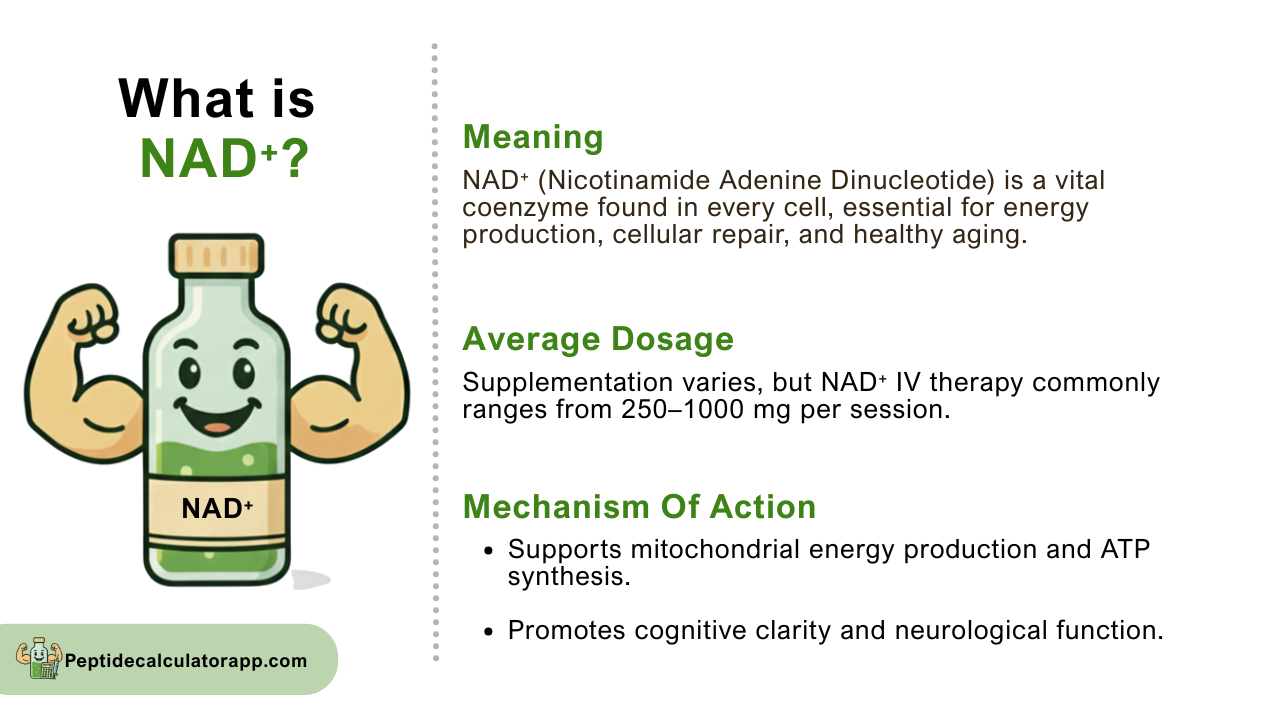
NAD⁺ is a vital coenzyme found in every living cell, serving as an essential component in numerous biochemical reactions. Discovered in 1906 by British biochemists Arthur Harden and William John Young, NAD⁺ functions as an electron carrier in metabolic processes, particularly in cellular respiration and energy production. The molecule consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups, with one containing adenine and the other nicotinamide.
The “+” in NAD⁺ indicates its oxidized state, meaning it can accept electrons from other molecules. When NAD⁺ gains electrons and a proton, it becomes NADH, the reduced form. This reversible reaction is fundamental to cellular energy metabolism, allowing cells to extract energy from nutrients and convert it into usable forms like ATP.
NAD⁺ levels naturally decline with age, dropping by approximately 50% between ages 40 and 60. This decline has been linked to various age-related health issues, making NAD⁺ supplementation and precursor therapies increasingly important areas of research and clinical application.
How NAD⁺ Works
NAD⁺ operates through several critical mechanisms within cellular physiology. As a coenzyme, it participates in over 400 enzymatic reactions, primarily serving as an electron acceptor in redox reactions. During glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NAD⁺ accepts electrons from glucose and other substrates, becoming NADH. This NADH then transfers electrons to the electron transport chain in mitochondria, ultimately leading to ATP production.
Beyond energy metabolism, NAD⁺ serves as a substrate for several important enzyme families. Sirtuins, a family of NAD⁺-dependent deacetylases, use NAD⁺ to regulate gene expression, particularly genes involved in stress resistance, metabolism, and longevity. The activation of sirtuins by NAD⁺ has been linked to lifespan extension in various organisms.
NAD⁺ also functions as a substrate for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), enzymes crucial for DNA repair mechanisms. When DNA damage occurs, PARPs consume NAD⁺ to facilitate repair processes. Additionally, CD38, an enzyme that increases with age, degrades NAD⁺, contributing to the age-related decline in cellular NAD⁺ levels.
The molecule’s role in maintaining circadian rhythms is another critical function, as NAD⁺ levels fluctuate throughout the day and help regulate the body’s internal clock through sirtuin activation.
Benefits of NAD⁺
Enhanced Cellular Energy Production
One of the most widely recognized benefits of maintaining healthy NAD⁺ levels is improved cellular energy output. NAD⁺ plays a central role in mitochondrial function and ATP generation, and when levels are optimal, cells are able to perform energy-dependent processes more efficiently. Many people notice higher physical stamina, reduced feelings of fatigue, and a general sense of increased vitality when NAD⁺ metabolism is supported.
Cognitive and Neurological Support
NAD⁺ has also become an area of interest in cognitive health research. Its involvement in neuronal energy metabolism and its ability to reduce oxidative stress make it important for long-term brain function. Some studies suggest that supporting NAD⁺ levels may help protect neurons, enhance mental clarity, and improve concentration. Although individual responses vary, many users report sharper focus and better cognitive endurance, especially during periods of high mental demand.
Anti-Aging and Longevity Effects
Perhaps the most publicized benefit of NAD⁺ is its potential role in slowing certain aspects of the aging process. NAD⁺ activates sirtuins, a family of proteins associated with longevity, cellular repair, and metabolic stability. As a result, higher NAD⁺ activity may contribute to improvements in skin appearance, muscle function, and overall metabolic health.
DNA Repair and Cellular Protection
NAD⁺ also supports DNA repair pathways, particularly through its involvement with PARP enzymes. This function is crucial for minimizing long-term cellular damage and maintaining genomic stability. Consistent NAD⁺ support may help reduce the buildup of cellular injury associated with aging, environmental exposure, and oxidative stress.
Dosage and Administration
NAD⁺ supplementation approaches vary significantly based on the specific compound and delivery method used. Direct NAD⁺ supplementation faces challenges due to poor bioavailability when taken orally, as the molecule is rapidly degraded in the digestive system.
NAD⁺ precursors represent the most common supplementation approach. Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is typically dosed at 100-300mg daily, while nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is commonly used at doses ranging from 250-1000mg daily. These precursors can cross cellular membranes more easily and are converted to NAD⁺ within cells.
Intravenous NAD⁺ therapy has gained popularity in clinical settings, with doses typically ranging from 250-1000mg per session. This delivery method bypasses digestive limitations and provides direct cellular availability, though it requires professional administration.
Sublingual NAD⁺ patches and nasal sprays offer alternative delivery methods that may improve bioavailability compared to oral supplementation. These approaches are still being studied for optimal dosing protocols.
Timing of administration can influence effectiveness, with many practitioners recommending morning doses to align with natural circadian NAD⁺ rhythms. Starting with lower doses and gradually increasing allows for tolerance assessment and optimization of benefits.
Storage and Stability
Proper storage of NAD⁺ supplements is crucial for maintaining potency and effectiveness. NAD⁺ and its precursors are sensitive to light, heat, and moisture, requiring specific storage conditions to prevent degradation.
Powder forms should be stored in airtight containers in cool, dry environments, ideally at temperatures below 25°C (77°F). Refrigeration can extend shelf life but may not be necessary for all formulations. Avoiding exposure to direct sunlight and humidity is essential for maintaining stability.
Liquid NAD⁺ formulations typically require refrigeration and have shorter shelf lives compared to powder forms. These products should be kept away from light and used within the timeframe specified by the manufacturer.
Reconstituted NAD⁺ solutions for injection must be used promptly, typically within 24-48 hours when stored under proper refrigerated conditions. These solutions are particularly sensitive to degradation and should never be stored at room temperature for extended periods.
Capsulated NAD⁺ precursors generally offer better stability than powder forms, with most products maintaining potency for 2-3 years when stored appropriately. However, checking expiration dates and storage recommendations on product labels remains important for optimal results.
Potential Side Effects
General Tolerance and Initial Adjustments
NAD⁺ supplementation is typically well-tolerated, but some users may notice mild reactions—especially when starting a new protocol or using higher doses. These early responses are usually short-lived and tend to diminish once the body adapts to increased NAD⁺ availability.
Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Digestive issues are the most frequently reported side effects. Some people experience nausea, stomach discomfort, or a bit of digestive upset, particularly with oral NAD⁺ supplements or precursors. These symptoms often improve when the supplement is taken with food, or when users begin with a lower dose and gradually increase it as tolerated.
Flushing Responses
A temporary flushing sensation may occur with certain NAD⁺ precursors, especially nicotinic acid–based forms. This reaction can involve warmth, redness of the skin, or a brief tingling feeling. Although harmless, it can be bothersome for some individuals. Switching to non-flushing forms of NAD⁺ precursors can usually eliminate this issue entirely.
Headaches and Fatigue
Ironically, headaches or mild fatigue can appear during the early stages of supplementation. These effects are thought to result from the body adjusting to shifts in cellular energy metabolism and increased repair activity. In most cases, they resolve naturally as the system stabilizes.
FAQs
Q1. How long does it take to see results from NAD⁺ supplementation?
Most users report initial energy improvements within 1-2 weeks, while more significant benefits may become apparent after 4-8 weeks of consistent use. Individual responses vary based on baseline NAD⁺ levels and overall health status.
Q2. Can NAD⁺ supplements interact with medications?
While generally safe, NAD⁺ supplements may interact with certain medications, particularly those affecting blood sugar or blood pressure. Consulting with healthcare providers before beginning supplementation is recommended for individuals taking medications.
Q3. Is it better to take NAD⁺ directly or use precursors?
NAD⁺ precursors like NR and NMN typically offer better bioavailability and cellular uptake compared to direct NAD⁺ supplementation when taken orally. Intravenous NAD⁺ bypasses absorption issues but requires professional administration.
Q4. Are there natural ways to boost NAD⁺ levels?
Exercise, caloric restriction, and certain foods like milk and green vegetables can support natural NAD⁺ production. However, supplementation may be necessary to achieve significant increases, particularly with aging.
Final Thoughts
NAD⁺/NAD represents a fundamental component of cellular health and energy metabolism, with research consistently demonstrating its importance in aging, cognitive function, and overall wellness. As our understanding of this crucial molecule continues to expand, its therapeutic potential becomes increasingly apparent.
The declining levels of NAD⁺ with age make supplementation an attractive option for many adults seeking to maintain optimal cellular function and support healthy aging processes. While research continues to evolve, current evidence suggests that maintaining adequate NAD⁺ levels through supplementation or lifestyle interventions may offer significant benefits for energy, cognition, and longevity.
As with any supplement regimen, consulting with healthcare providers and choosing high-quality products from reputable sources remains essential for optimal results and safety. The future of NAD⁺ research promises to further illuminate its therapeutic potential and refine our understanding of optimal supplementation protocols.




